
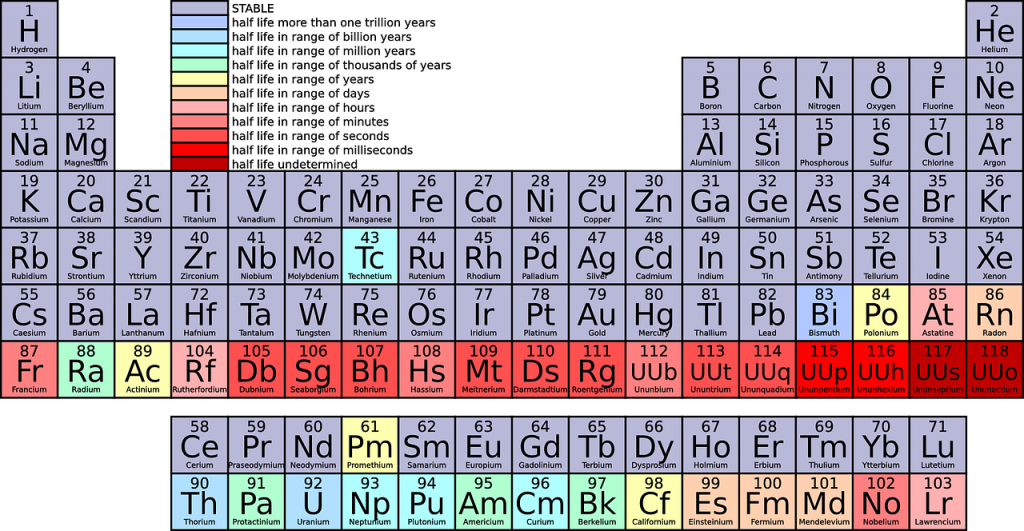
The underlying factor that largely dictates an element’s properties is the number of electrons that orbit in the shell furthest form the nucleus. We now know the reality is more sophisticated.
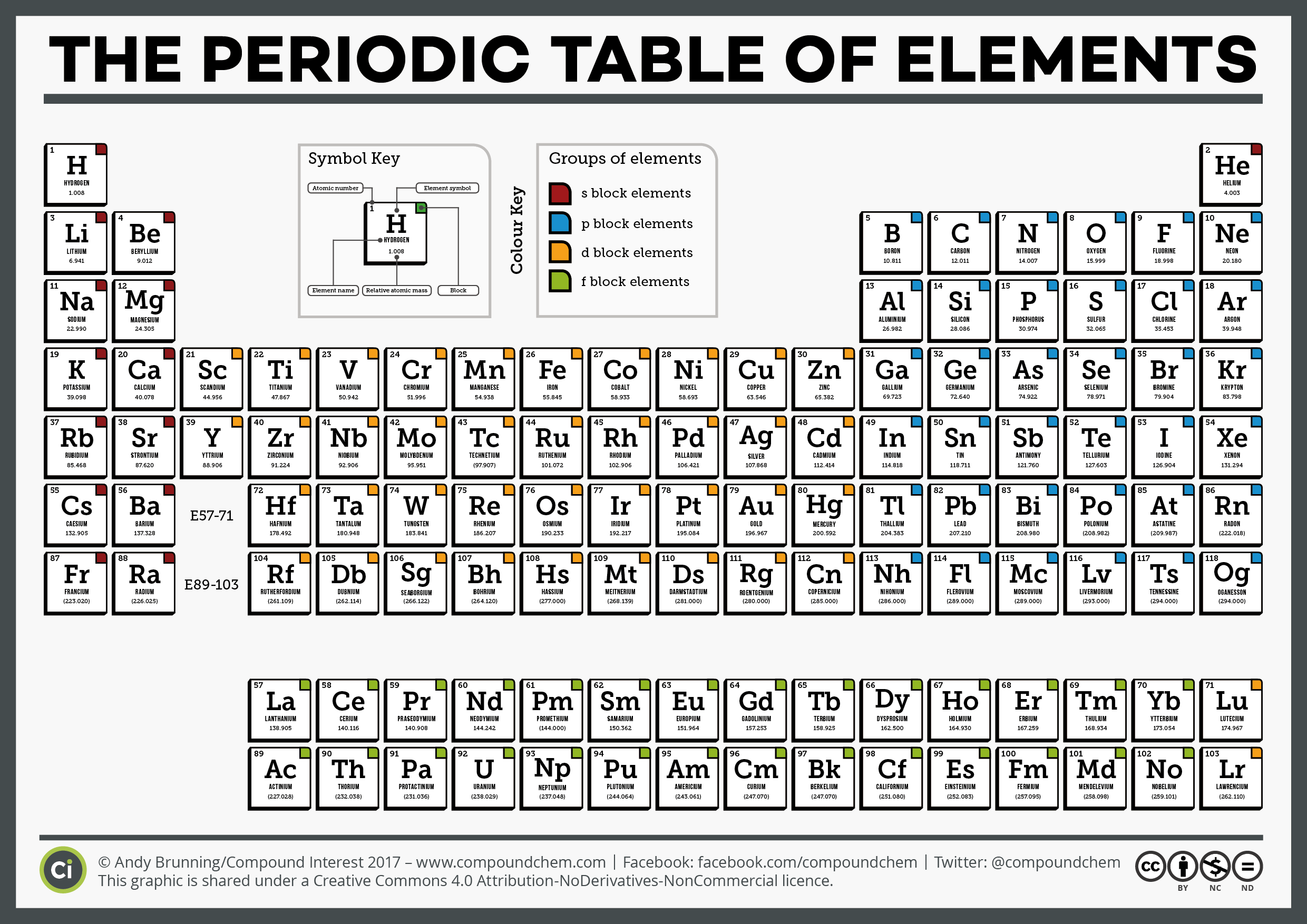
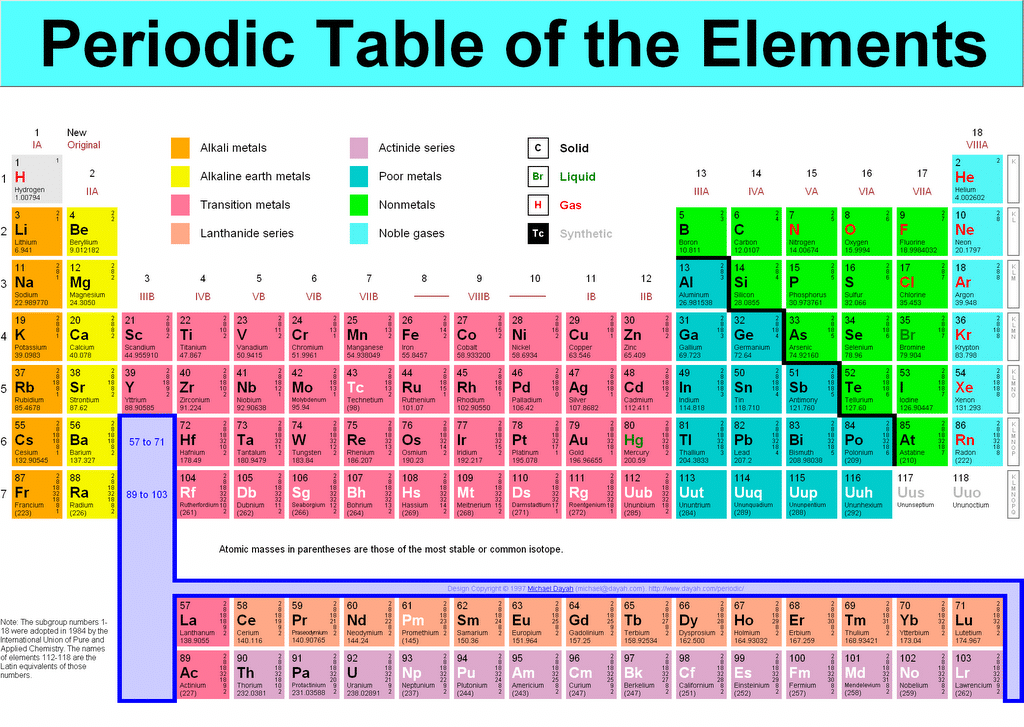
In tribute to this musical analogy, the chemists who first noticed the pattern in the elements more than 150 years ago called it the law of octaves. As you hit the eighth note, something beautiful happens – a note hangs in the air that embodies something of the first. The notes flow out, resounding at a higher and higher pitch as your hand moves to the right. Lithium, for example, with an atomic number of 3, is a reactive metal - just like sodium (element number 11) and potassium (number 19).Ī good way to think about it is to imagine running your fingers over the keys of a piano. As you keep adding protons, you find that similar properties recur in every 8th element. If you have one proton, that is hydrogen. Periodic Table Alkali metals Alkaline earth metals Transition elements Halogens Nonmetals Inner transition elements Metals Metalloids Noble gases. It is the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, known as its atomic number, that determines which element it represents. The periodic table is a physical representation of two more abstract notions, namely the periodic law and the periodic system, both of which are more. The periodic table captures a subtle pattern that runs through the chemical elements, the fundamental building blocks of everything around us: from the aluminium in bike frames to the xenon gas in glowing shop signs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
